
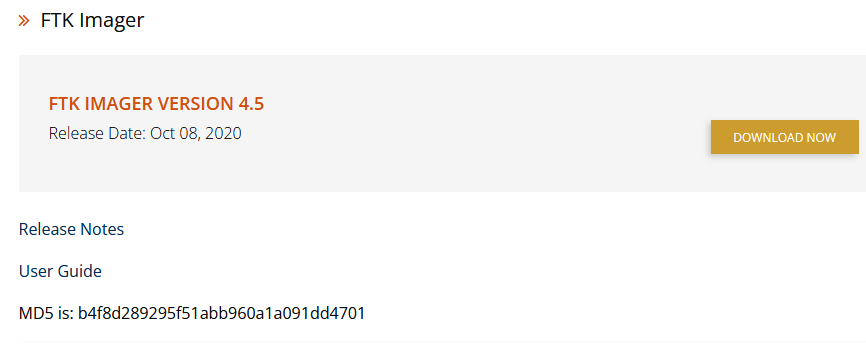
Make sure the “verify images after they are created” check box IS checked and click start. Now that you have the destination set it’s about time to start the image acquisition. If the destination location is larger than the drive being image set to zero and it will be done much quicker otherwise the default setting of 6 is a good compromise between speed and size. Compression can make this significantly smaller at the expense of speed, compression takes time. A raw disk image without compression will be the exact same size as the hard drive you are imaging, 500GB hard drive equals 500GB image file. Compression is used to make the image smaller. Image fragment size indicates how large each piece of the image will be and is used to ease file copy and transfer, leave it at the default size of 1500. Enter the file name of the image, here we will use example-case-001. Click next.Ī image destination dialog box will open, select the destination folder, make sure you have enough space there, images are large. Enter any notes if you need to, in this example we will leave it blank. The examiner field should be who is examining this case or evidence item, Insert your name here.
In the unique description field enter a description of the evidence, in this case we will enter “subject 1 hard drive from workstation”. Next add the evidence number, this is important if you are working a big case with multiple machines that need to be imaged enter HD-001 in this field since this is the first piece of evidence. Enter the case number or a unique identifier example-case-001 is a good choice for this lesson. Now we will add some pertinent information about the case we are working. The next dialog box will ask what type of image type, select E01 and click next. Next the application allows you to select the destination, click add. The next dialog box will ask you to select the drive you want to image, select the appropriate drive from the drop down and click finish. A dialog box will open allowing you to select the source type, in this example select physical drive and click next. When the application has opened select the file menu and then click create disk image. Once the drive is attached to the imaging machine launch FTK Imager. now connect the usb cable from the dock to the write blocker.connect the usb cable from the write blocker to the imaging machine.I recommend the Thermaltake dual hard drive docking station for attaching 2.5 and 3.5 inch SATA drives and SSD’s to the write blocker, it can be had for about 50 dollars on Amazon. Additionally, you will need a few adapters to connect the drives to the write blocker. A Wiebetech USB Writeblocker can be purchased from Amazon for around two hundred dollars and is the main component in the system. I will cover an inexpensive setup that is easy to use and will cover most devices you may run into. You can also just mount the disk in read only mode and image that way, but I do not recommend it. There are several companies that make them with the most popular being Tableau and WiebeTech, ranging from several hundred to several thousand dollars. The image acquisition process should ensure the original drive remains completely unaltered, and to make sure a hardware device called a write blocker is normally used. Attaching the drive with a write blocker.Character sets: ANSI ASCII, IBM ASCII, EBCDIC, (Unicode).Convert between binary, hex ASCII, Intel Hex, and Motorola S.
Erase (wipe) confidential files securely, hard drive cleansing to protect your privacy.128-bit encryption, checksums, CRC32, hashes (MD5, SHA-1.Programming interface (API) and scripting (professional & specialist licenses only).Drive images & backups (optionally compressed or split into 650 MB archives).
#HD FTK IMAGER DOWNLOAD LICENSE#
An advanced tool for everyday and emergency use: inspect and edit all kinds of files, recover deleted files or lost data from hard drives with corrupt file systems or from digital camera cards. WinHex is a universal hexadecimal editor, particularly helpful in the realm of computer forensics, data recovery, low-level data processing, and IT security.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
